
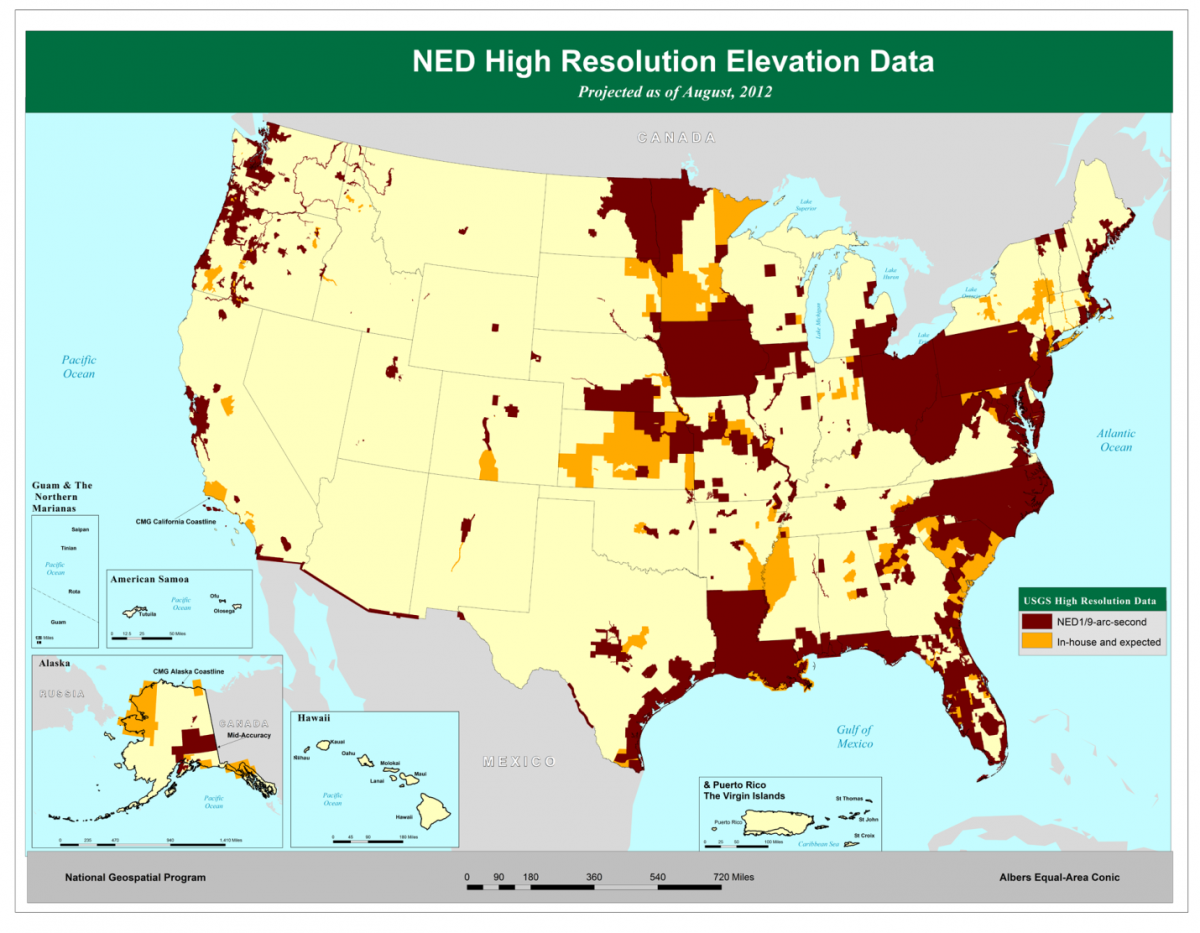
The NED is a collection of elevation data which covers the entire United )įor this exercise we will use elevation data from the National Elevation Dataset
#Usgs raster data download
You will not be able to download data in Internet Explorer. (In this part of the exercise, you should be using Mozilla Firefox as your browser. Programs > ArcGIS, except ArcToolbox, which is accessible from ArcMap. This is accomplished with the "Projectįor this lab you will download the necessary data from the web, as detailedĪll of this exercise can be done in the ArcMap, including ArcToolbox, and ArcCatalogĮach application can be found in the Start menu, under: Start > All Projection into another projection, the location of each point (vertex, grid-cell,Įtc.) in the dataset must be re-calculated. Information in the Layer Properties Dialog to find projection information.Ĭhanging a Projection - To project a dataset from its present To check if a dataset has a projection defined, look at it's metadata usingĪrcCatalog, or load it into a data view in ArcMap, and look at the Data Source Not change the dataset, it simply attaches projection information to the data. This can be done most easily with the "Define Projection

If not, the user must define the projection May or may not have a projection defined. If not, it will guess atĭefining a Projection - When a dataset is first acquired, it So long as the datasets have a projection defined. It will then re-project each dataset on the fly to match that projection, In ArcGIS these tasksĪre often done in the background, so the user does not have to worry about them.ĪrcGIS will use the projection of the first dataset loaded to set the projection In order to line up properly with all the other datasets. All the data in a GIS data view must be in the same projection We need to know what projection it is in, so that it can be properly aligned To transfer the geographic coordinates of latitude and longitude on the three-dimensionalĮarth to X and Y coordinates on a flat piece of paper. Projections - Every spatial dataset is projected in some manner, You will create a map showing both projections In this exercise, you will work with projections, by re-projecting a grid datasetįrom one projection into another. Projection Exercise - Downloading and projecting Digital Elevation Models (DEM)
#Usgs raster data software
The implementations of these methods are provided in an open source software package called MapImage (or mapIMG, for short), which is designed to function on a variety of computer architectures.Downloading and Projecting USGS Digital Elevation Models To address these problems of projection and the associated resampling that accompanies it, methods for framing the transformation space, direct point-to-point transformations rather than gridded transformation spaces, a solution to the wrap-around problem, and an approach to alternative resampling methods are presented. The accuracy of areas in projected raster datasets of global extent is dependent on resolution. Distortions associated with the reprojection of global data are generally greater than distortions associated with reprojections of larger-scale, localized areas. The distortion characteristics of these projection transformations can have significant effects on modeling results.
Such use often requires the projection of global raster datasets onto a map or the reprojection from a given map projection associated with a dataset. Scientists routinely accomplish small-scale geospatial modeling using raster datasets of global extent. Raster data, map projection, transformations Abstract USGS, Earth Resources Observation and Science Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota Geological Survey (USGS), Center of Excellence for Geospatial Information Science (CEGIS), Denver, Colorado


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
